RZA, the legendary co-founder of Wu-Tang Clan, is coming from a beat-making workshop at Williamsburg’s new Apple Store. He sounds upbeat as he describes how far music production technology has evolved since he started out. But in a throwback to the late 70s, a halcyon era for kung fu cinema more than a decade before Wu-Tang was formed, RZA is traveling the country performing a live re-scoring of classic Shaw Brothers martial arts film, The 36th Chamber of Shaolin.
During a live screening of the film, RZA constructs his own score from a collection of custom audio files. Growing up in Brooklyn, RZA became a sort of expert on martial arts films from the 70s and 80s. This infatuation eventually leaked into his work as a music producer where he would construct beats that incorporated movie music and dialogue. Now, armed with a Wu-Tang catalog over two decades in the making, RZA is reimagining the film’s score in real time, creating a composite audio-visual experience blending genres, cultures, and eras.
Videos by VICE
The Creators Project talked to RZA about his relationship to the film, his production process, and how he got into scoring cinema:

Screenshots via
The Creators Project: What’s your live-scoring setup like? Are you playing Wu-Tang samples over the original score?
RZA: Well, check it out [on tour]. I’ve been hooked up the Shaw Brothers. They gave me the film and let me strip it down.
They let you strip down the audio?
Yeah, instead of using the original score. I mean, there’s a few pieces that I liked and kept, but the majority of it is me. There’s about 90 sound cues in the film, and I’ll be manipulating those cues in real time.
Wow, that sounds like a lot to manage.
It took a minute to get it to where we got it. I had some good buddies help me on the technical side when we were putting it all together. But you know, when I was in about ninth grade, we were all DJing, battling each other, and trying to be the best. There was this one kid who couldn’t really DJ. He had the turntables, he had a system, he could mix, but he couldn’t scratch. He was cool—he ran with us—but what he used to do was plug into a VCR and then dub the VCR to another tape. So, for example, you’d see Wile E. Coyote chasing The Road Runner, and then they’d fall off a cliff, and he would pause it and rewind it, like a pause tape. He was the first kid I ever seen do that. But when DVDs came out, I was like, “Wow, now we can really do the shit that he was doing.” It could physically be done.
So I started practicing that, and I was probably one of the first guys to do that. Of course, I’ll say I learned it from my man Tom Shannon when I was a kid. I saw him do it. But now technology has caught up to where they got it all inside the software. When the time came for me to do this, I called Tom and had him come help me. He helped me break it down, decide on certain things, and help me get to a point where I could sit there and just do it. It’s crazy how full circle it is: from seeing this movie as a kid, to becoming a young adult and using it as the title for my first album. You never know what part of your childhood, or of your life, will inspire something else.
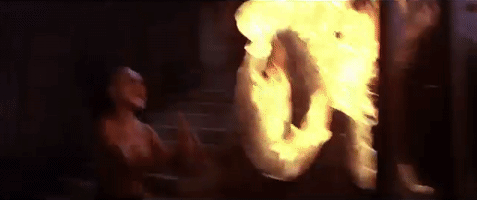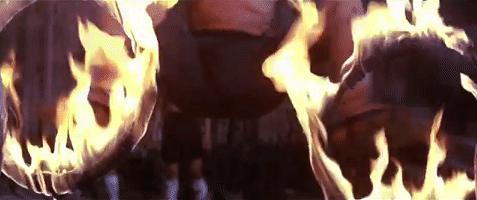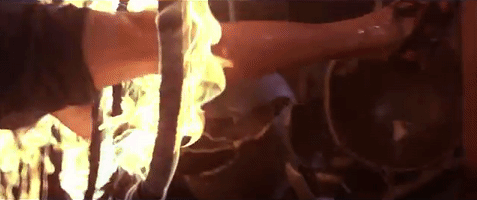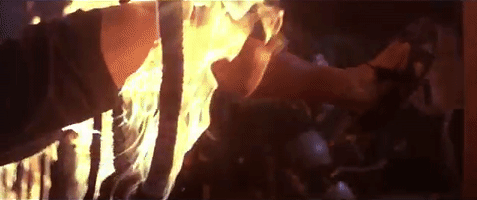
What aspect of martial arts films inspires you musically? The writing, cinematography, or the action?
The action was the first attraction. That’s a rhythm within itself. I became aware of the cinematography later on. 36th Chamber is one of the films that opened my eyes to cinematography and the vastness of what it could be. Take Into The Dragon, for example: Bruce Lee was great, and all that. But it was set way in the past, and the director happened to be considered one of the best directors of Asian cinema—of any cinema. But then the music happened. The emotions of the music started resonating with me. And for me, with hip-hop, I have to take that music and pin it to a groove—my drum pulse.
So that’s what I started doing, started plugging my VCR into my sampler. I could sample a strange part, with a vibe-heavy rhythm. Or I could just take an intro, like in the song “Da Mystery Of Chessboxin,” where he’s like, “Toad style is immensely strong and immune to nearly any weapon. When it’s properly used it’s almost invincible.” That felt dangerous, deadly, and that’s what Wu-Tang was bringing: rugged, raw, deadly hip hop. And thinking about martial arts movies and the ideas of swordsmen, there was no better way to make the analogy of how deadly we are than through martial arts films.
What was your relationship to 36th Chamber when you were growing up in New York?
Well, I grew up in the 70s, you know. When this movie came out and I saw it, at the top ot the 80s, I was becoming conscious of oppression and the black man’s struggle in the world. It seemed similar; it felt like, “Why us?”
In the film, these people are being oppressed and are struggling. They came and killed [the main character’s] father for nothing—just stabbing people. He had to run for his life, and he was just a student, a college student, who wanted to make a change, you know? It made me think about college students in the 60s who tried to march and change the world and got fire hosed down and attacked, you know what I mean? At the time, I thought that stuff only happened in America, in this time period. But the film was one of the things that opened my mind to the fact that this happens around the world. I related to that shit. I was like, “Wow, I feel him. I understand his struggle.” I also wished there was something I could learn to help my people.

Still from ’36th Chamber.’ Courtesy the Alamo Drafthouse Cinema
How is producing a song in the studio different from producing a score for a film?
Let’s say I’m doing something for Wu-Tang: I’ll pick the music because I know the talent. When I did my first score with Jim Jarmusch for Ghost Dog: The Way of the Samurai, I didn’t really know what I was doing. I studied Peter and the Wolf, and I understood that I could pick different instruments to represent different characters, but I didn’t really understand the whole post-production process. Jim didn’t force me to sit there and go through that. But on Kill Bill, Quentin Tarantino did make me sit there. I had to sit in the editing room for probably 60 days. It was cool, it was a great experience; you couldn’t beat me and Quentin in the editing room together. But at the same time, the amount of stuff I learned was wild. Instead of being the producer and the leader, I had to be more subservient to the director’s wishes.
But it still took time, you know, for me to understand that I have to deliver that vision. Now, as a person who has the capability—who has proven himself—I can approach the production of songs like I approached the score for my own film, The Man with the Iron Fist. Now, I strive to make sure the artists are embellished, and when I’m scoring a film, I also strive to make sure the emotions of my characters are being embellished.

How does the process change when you’re doing it live, as opposed to spending, for example, 60 days in the editing room ensuring everything is perfect?
Well, it’s live in the sense that I’m doing it live, but it’s rehearsed. We’ve combed through what we think will work. This will be my fifth time doing this performance, and I think it only gets better every time, because I’ve learned what doesn’t work.
I learned that 110 cues was too much. I was overkilling it. I’ve got to let it breathe. At one moment I’m just doing me, and then I’m like, “Wait a minute, I forgot about the film.” That happened in Austin, and even though the crowd gave a standing ovation, I felt like I forgot about the film. By the time I got to LA, I kind of had a better format, I let it breathe, and I think it performed better. I think in New York, it’s going to be even better.
RZA: Live From The 36th Chamber plays at The Town Hall Thursday, November 10 at 8pm. Visit the Alamo Drafthouse Cinema website for future performance dates.
Related:
Fans Order Feds to Release Martin Shkreli’s Wu-Tang Clan Album
RZA Becomes a Monk in a New Photo Series
Now We Know Which Rapper Has The Largest Vocabulary In Hip-Hop



